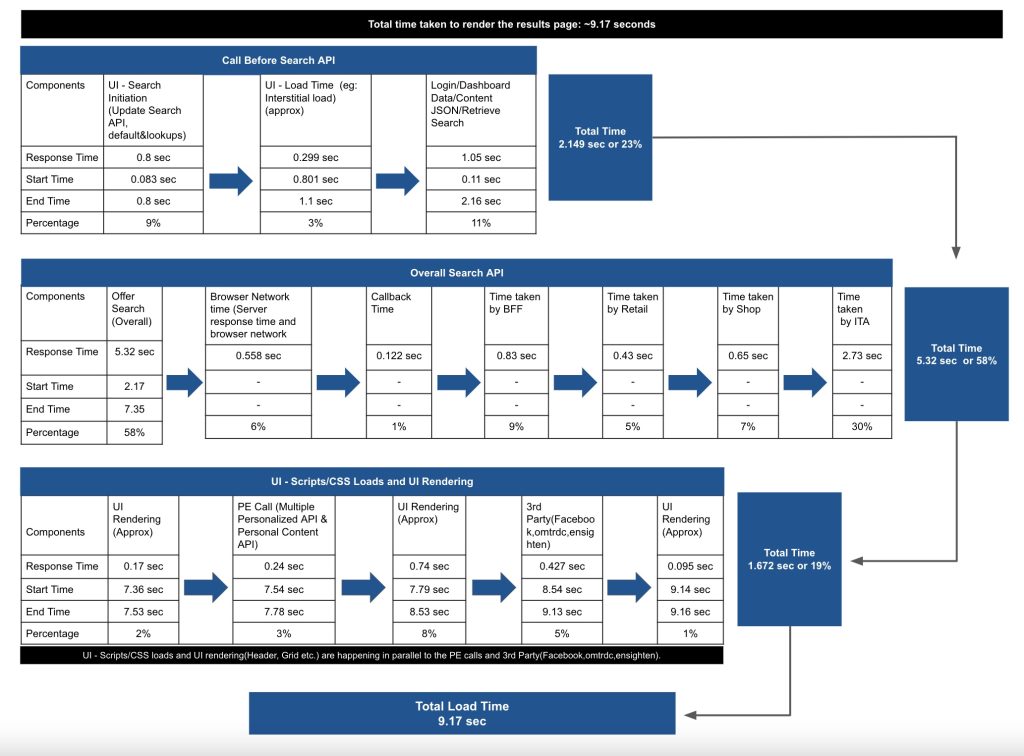
Overview
Normally, when a user opens a webpage, the entire page’s contents are downloaded and rendered in a single go. While this allows the browser to cache the web page, there’s no guarantee that a user will consume all of the data that is downloaded onto a page. Thus slowing the download speed of the page down. Instead of dumping all the content on one single load, the content will load when the user accesses part of the page when called. With lazy loading, pages are created with placeholders and displayed when inside the user's viewpoint.